Enabling dbt Features in Etleap
To enable dbt features that allow you to edit models, create schedules, and run preview CI builds, complete the following setup.
Etleap can connect to one dbt project repository that is hosted in GitHub.
Step 1. Install the Etleap GitHub App in your repo
Log in to Etleap and navigate to the Admin Console. Select dbt Settings and complete the GitHub app installation wizard.
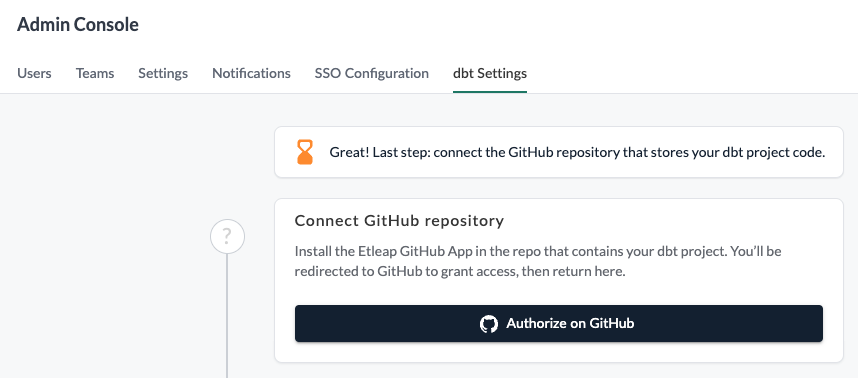
To install the Etleap GitHub App, the user initiating the installation in Etleap must have admin permissions on the target GitHub repository.
Step 2. Connect a Warehouse for CI
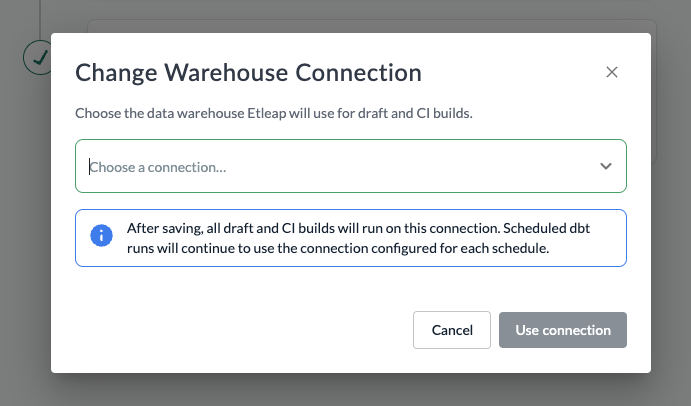
In order to run CI and draft builds, Etleap needs a default warehouse connection which it will create a temporary schema in to test the builds.
To setup CI and draft builds, select a warehouse connection on the dbt Settings screen.
Step 3. Create your dbt Project
To use dbt features, your main branch must contain a valid dbt project.
A valid dbt project is one in which dbt parse runs successfully.
At a minimum, the project must:
- Include a dbt_project.yml file in the project’s root with required configuration defined
- Include a models folder, for either the default
/modelspath or the first path defined in the[model-paths]field of yourdbt_project.yml - Ensure all
ref()andsource()Jinja calls point to existing models or sources - Include any macros referenced in models in the project or imported packages
Uninstalling the Etleap GitHub App
To uninstall the Etleap application from your GitHub repository and organization, first disconnect it from the dbt Settings tab in the Admin console.
After disconnecting, Etleap will no longer have access to your repository.
The Etleap GitHub App will still appear as installed in GitHub. To fully remove it, go to Settings > Integrations > GitHub Apps and follow the uninstall instructions.