dbt Editor
The dbt Editor is a streamlined SQL editor that allows you to easily create and modify dbt models without a local development environment or prior knowledge of dbt Core or Git.
Model Editing
The dbt Editor provides a view that contains your existing models, a SQL editor pane, and model dependency information.
Pipeline Mapping
The dbt Editor has full context of your existing Etleap pipelines and uses this to auto-detect when a source in a model you’re editing matches one of your pipeline destination tables.
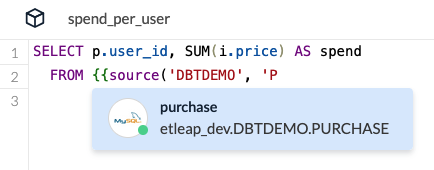
Materialization
Models created with the dbt Editor will follow the materialization configuration hierarchy defined by your dbt project.
Language Support
The dbt Editor supports creating models that contain SQL and Jinja.
Preview Builds
Preview builds allow you to review the output of your model as you build. Every time your draft is saved, dbt CI builds are run. The dbt Editor provides the status of these runs and quick access to the build logs once completed.
File Management
The dbt Editor allows you to create .sql model files and will automatically generate a .yml sources file if needed.
Model Files
Model file names may contain lowercase alphanumeric characters and underscores.
All model.sql files that are created by the dbt Editor will be placed in the first path of the model-paths array defined in your dbt_project.yml file.
If the model-paths array is not defined, the /models path will be used.
If an existing model, defined as /model-path/sub-path/model.sql, is renamed it will remain at the same path and become /model-path/sub-path/renamed-model.sql.
Sources Files
When using the dbt Editor, Etleap manages a sources file called _etleap_sources.yml. This file contains sources for all of your Etleap pipeline destination tables that are in the same warehouse as your dbt models.
The _etleap_sources.yml file will be created in the first path of the model-paths array defined in your dbt_project.yml file.
If the model-paths array is not defined, the /models path will be used.
Version Control
Any change that is saved in the dbt Editor is synced with your organization’s GitHub repo. The different model save actions and their corresponding handling in Git are described below.
| dbt Editor Action | Description | Git Action |
|---|---|---|
| Start Draft | You begin editing a model draft, but have not yet saved | Not tracked in Git |
| Save as Draft | You clicked the Save as Draft button in the editor and a preview build is initiated | The model changes are committed to a new draft branch and a pull request (PR) is opened |
| Update Draft | You make additional changes to your model and click Update Draft | An additional commit is made to the draft branch in Git |
| Publish Draft | You finalize your model and click Publish Draft | The PR is merged into the main branch and the draft branch is deleted |
| Delete Draft | You select Delete Draft from the overflow menu to discard changes | The draft branch is deleted and the PR is closed |
You cannot create dbt Schedules for models that have not yet been published.
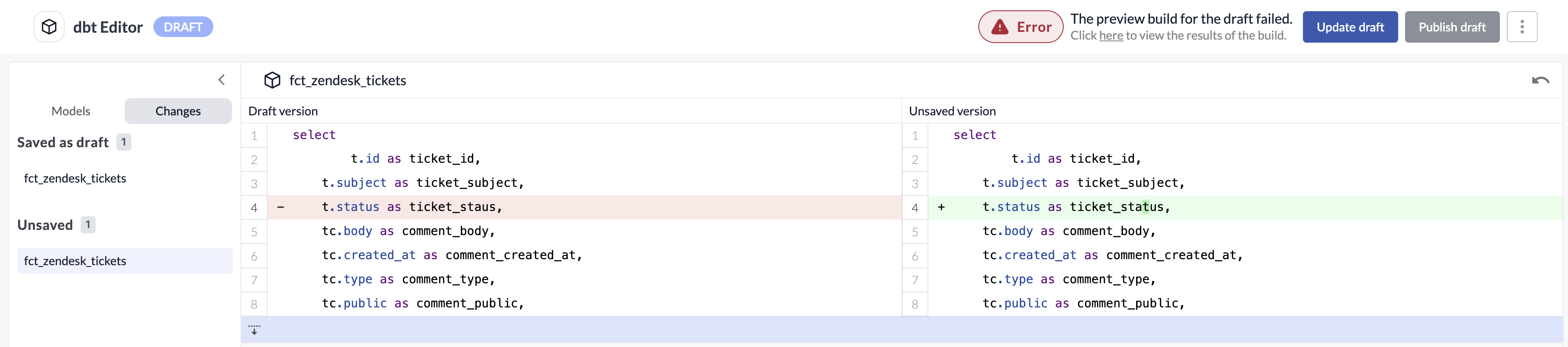
File Changes
Once you have modified files in the dbt Editor, you can review the changes that have been made. These changes are split into two categories:
- Saved as Draft: Changes have been saved as part of the current draft, but have not yet been published.
- Unsaved: Changes have been made to the file, but have not yet been saved to the draft.
Git Conventions
As you create and update models, the dbt Editor automatically creates the following Git objects and references.
Branches
The Git branches that Etleap creates for new drafts follow the format etleap-editor/<clean_user_name>/<YYYMMDDHHMMSS>.
Where clean_user_name is the Etleap user’s name with any special characters replaced by -.
The timestamp in the branch name is when the user created the draft in Etleap.
Any branch created by Etleap will also be cleaned up by Etleap as described in the Version Control table.
Commit Messages
Commit messages created by the dbt Editor will use the following formats depending on the actions taken by the user:
- Added X, Y, and Z.
- Updated X, Y, and Z.
- Renamed X to Y, Y to Z, and Z to X.
- Deleted X, Y, and Z.
Commits made while saving and updating a draft will be attributed to the user in Etleap that saved the draft in the format of <Etleap user's name> (Etleap user's email).
If the email address used for Etleap is also used by an active GitHub account, commits will be associated with that GitHub user automatically by GitHub.
Merge commits made to the main branch, when drafts are published, are associated with the Etleap-owned GitHub user you provided repo access to while enabling dbt features.
Pull Requests
The pull requests created by Etleap will have titles that follow the format Etleap Editor - <short change summary> - <YYYY-MM-DD>.
The short change summary will either be:
model name, if a single model was updated.# models updated, if more than one model was updated.
The body of the pull request will contain:
Created automatically via Etleap's dbt Editor.
Author: <Etleap user's email address>PRs created by the dbt Editor are associated with the Etleap-owned GitHub user you provided access to while enabling dbt features. The body and title of the PR will not be updated after the PR is initally opened when you first save a new draft. The PR title and body can be safely modified in from GitHub later.
Any PR opened by Etleap will also be closed automatically by Etleap, as described in the Version Control table.
Draft Errors
If your draft errors due to a conflict with the currently published version of your models, you won’t be able to publish it. To proceed, either resolve the merge conflict in GitHub or delete the draft and start a new one.
Scheduling Models
After publishing the models in the editor, you can create a dbt Schedule to periodically build them in your warehouse.
To create a dbt Schedule from your models, you will first need to define a selector in the selectors.yml file in your dbt project.
The dbt Editor creates new models in the first directory listed in the model-paths property in the dbt_project.yml file.
To create a selector that includes only the models at this path, you can add the following to the selectors.yml file:
selectors:
# ... other selectors you may have previously defined ...
- name: select_root_models
description: Includes all models in the root models directory.
definition:
method: path
value: "<your-model-path>/*.sql"Where <your-model-path> is either
- the first path defined in the
model-pathsconfiguration in yourdbt_project.ymlfile, or modelsifmodel-pathsis not specified.
The selectors.yml file must be created and edited outside of Etleap.
Creating and editing YAML files directly in the dbt Editor is not currently supported.
Limitations
- To provide compatibility with all data warehouses, model file names must be no more than 115 characters. For compatible warehouses, model aliases may be used to allow for the database object’s name to exceed this limit.
- Non-model files cannot be accessed from the dbt Editor.
- Models cannot be created in a directory other than the default
models-pathof the project. - Python models are not supported.
- Since Etleap adds all eligible pipeline destination tables as sources to the
_etleap_sources.ymlfile, you cannot have tables that are loaded to by Etleap in any of your other sources files. - There must be no schema-level naming conflicts between the sources in your project.
- The dbt Editor can only read and write to a single GitHub repo.
- The GitHub repo you connected during setup must have a valid dbt project in it to use the dbt Editor.
- The model editor does not support referencing schemas or tables that contain double quote (
") or backtick (`) characters.