dbt Schedules
Overview
Dbt Schedules let you build end-to-end data pipelines in Etleap that involves both data ingestion and data modeling.
Dbt Schedules run on a user-defined cron schedule , triggering pipeline runs that extract new data from the source, transform it, and load it into your warehouse. Once the data is loaded, a dbt Schedule triggers new dbt builds, executing post-load transformations of your warehouse’s data. You can use dbt Schedules in Etleap to combine ingested pipeline data with other data in your warehouse. Dbt Schedules and end-to-end data pipelines allow you to reason about the latency of the final data model.
Etleap’s dbt Schedules support setting up end-to-end pipelines for Redshift, Snowflake and Databricks Delta Lake warehouses.
Example Sequence
The graphic below shows how you can use dbt Schedules to enable end-to-end data pipelines that model data from different sources in your data warehouse. The following sections outline the different steps of the end-to-end pipelines in the graphic:
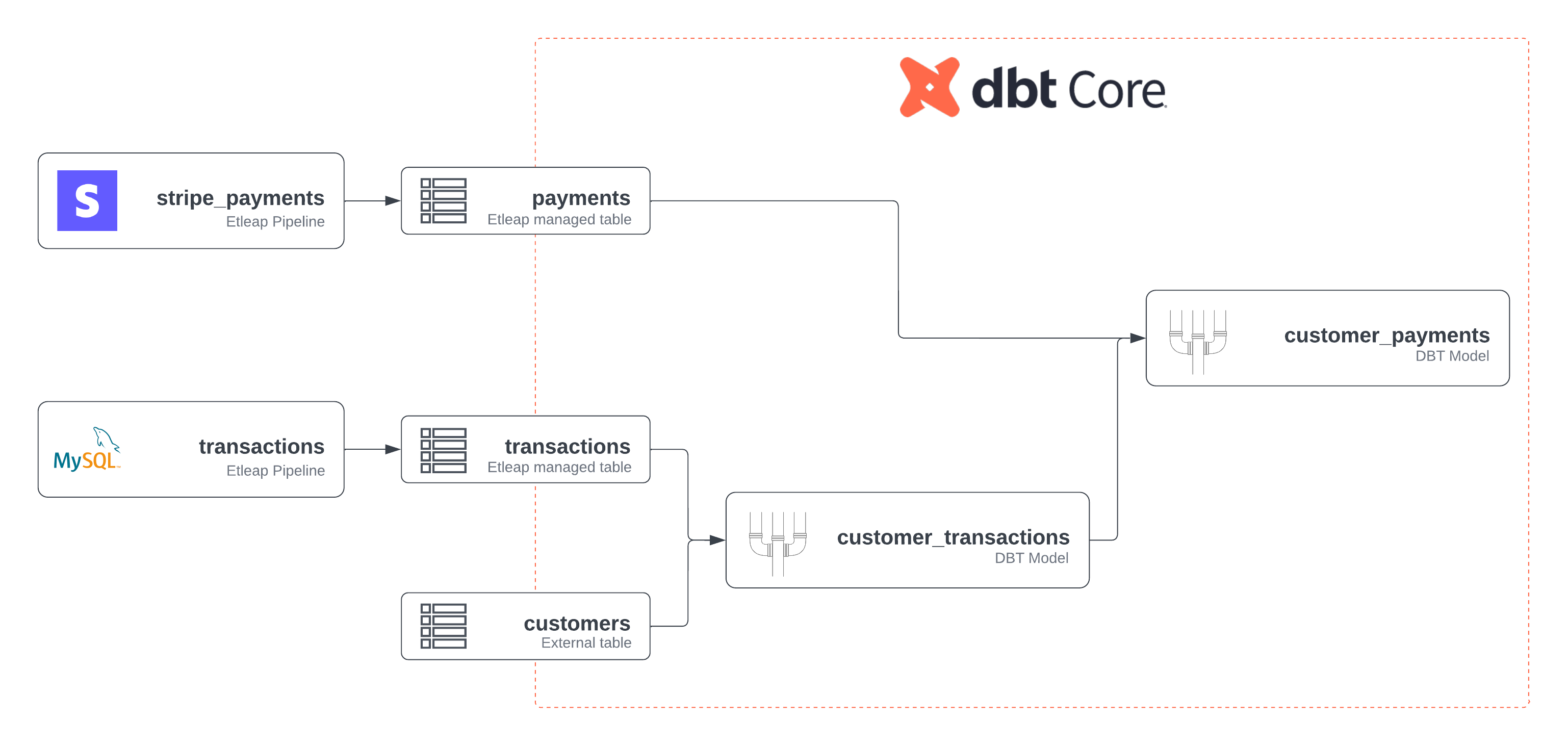
Etleap Pipeline Runs
In this example, Etleap is ingesting data from Stripe and MySQL, and loading to managed destination tables. These pipelines run based on the dbt Schedule’s cron schedule. Once these pipelines finish loading, the models will begin building.
dbt Modeling
The destination tables from the Stripe and MySQL pipelines are specified as dbt sources in the dbt project. These sources are referenced by the “payments” and “transactions” models.
External tables in the warehouse that are not managed by Etleap, such as the “customers” table, can also be referenced as dbt sources in your dbt models.
Etleap is aware of which models reference other models; this is used to generate the directed acyclic graph (DAG) shown in the Schedule Overview page of the UI. In this example, the output of the first dbt model (“customer_transactions”) and the Etleap-managed Stripe destination table are both used in a subsequent model, called “customer_payments”).
After the Stripe and MySQL pipelines ingests data into the warehouse, the dbt Schedule’s cron schedule triggers a dbt build that creates the model in your warehouse.
You can find out how to set up a dbt Schedule here.
dbt Schedule Latency
End-to-end data pipelines allow you to reason about the latency of the final data model. You can view which pipelines are still waiting to ingest, before your models can be built, in the schedule’s activity feed.
Components of a dbt Schedule
Dbt Schedule runs consist of 3 stages: the dbt Schedule trigger, the pipeline runs, and the actual dbt build.
Triggers
A dbt Schedule triggers if any of the following conditions are met:
- Immediately after the dbt schedule is created.
- Immediately after a new commit is pushed to the main branch.
- Immediately after manually triggering the schedule using the UI or the API .
- According to the cron schedule you’ve set, assuming there is no other dbt run in progress.
Pipeline Runs
Once a dbt Schedule triggers, pipelines that are part of the dbt Schedule (via automatic source mappings) check for new data in the source. If there is new data, pipelines will extract, transform, and load it to the pipeline’s destination. This stage is complete when every referenced pipeline has successfully completed its run, established there is no new data in its source, or is stopped for any reason (e.g. the source connection is down, or waiting for a schema change to be applied manually).
When a pipeline is referenced by a dbt Schedule, the pipeline’s runs are throttled by the pipeline’s Update Schedule. In other words, at this stage, the pipeline’s run will be blocked until it is allowed by the pipeline’s Update Schedule. Note that this may cause delays to the dbt Schedule run as a whole.
For pipelines that ingest into a destination with a Load Throttle set, the Load Throttle is ignored when the pipelines are a part of a dbt Schedule.
Dbt Builds
Once the pipeline run stage is complete, Etleap triggers a dbt build to create models, run tests, generate snapshots, and load seeds.
Skipping the dbt build
A dbt build is skipped in the following cases:
- There has been no new data for each of the dependent pipelines since the last build and the flag to skip dbt builds when there is no new data is set.
- One or more of the dependent pipelines are stopped or paused and as a result, source table data may not be up-to-date.
The first build for the schedule and any builds triggered due to updates to the dbt project code will not be skipped when skip dbt builds when there is no new data is enabled. However these can still be skipped due to dependent pipelines that are stopped or paused. In this case, the dbt build may then be retried during the next scheduled trigger.
A manually-triggered build is never skipped.