SQL Server: Configure Transaction Log Retention
Check Which Type of Replication is in Use
Before configuring log retention, first check whether the source is using MS-CDC or MS-REPLICATION to replicate changes to Etleap.
Run the following SQL query to see whether the CDC capture job is running for the database:
USE <db name>;
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_help_jobs;If MS-CDC is enabled on the source, you should see an entry where job_type is capture.
In this case, the capture job can be configured directly.
If there is no capture job present, then MS-REPLICATION is being used and Etleap’s CDC process will use a Log Reader agent installed on the source to capture changes.
In this case, the Log Reader Agent must be configured via SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
If both MS-REPLICATION and MS-CDC are in use, the Log Reader Agent will be solely responsible for reading from the transaction log and you should follow the MS-REPLICATION steps below.
Configure Log Retention
Follow the steps for either MS-REPLICATION or MS-CDC depending on which is in use on the source.
using MS-REPLICATION
Step 1. Review the Recommended Configuration Settings
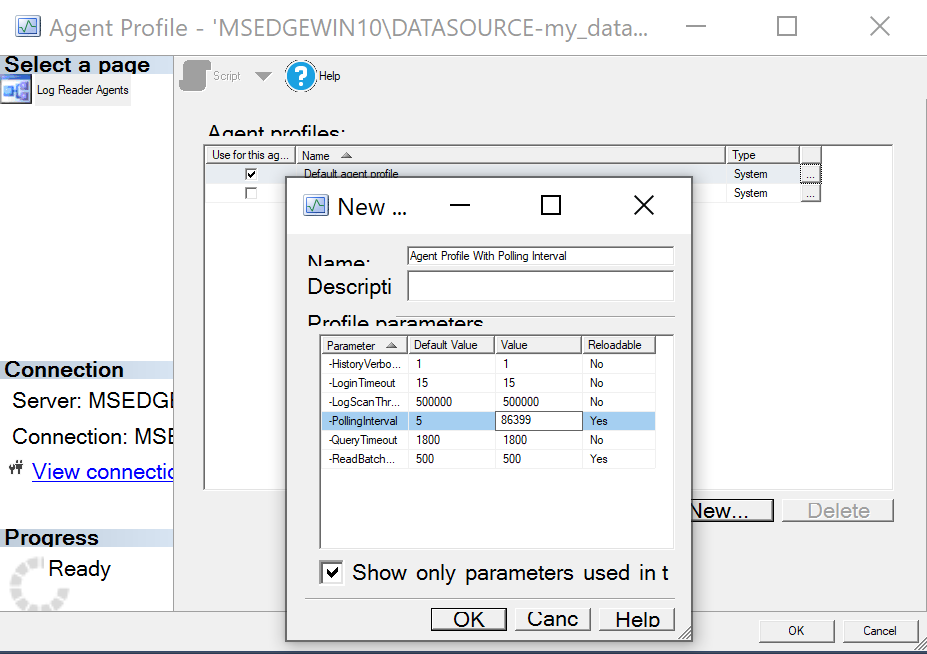
To configure log retention when MS-REPLICATION is in use, you need to configure the PollingInterval and ReadBatchSize properties on the Log Reader Agent.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
ReadBatchSize | The maximum number of transactions read out of the transaction log of the publishing database per processing cycle. |
PollingInterval | The number of seconds to pause after the job runs. |
There are some trade-offs to consider when choosing values for the above properties:
- If the
PollingIntervalis too low, changes will be removed from the active transaction log before the CDC process can read them. - Decreasing the
ReadBatchSizemeans that the Log Reader Agent will take longer to move transactions to the distribution database and therefore replication latency will increase. - Performance can be improved by increasing
ReadBatchSizefor workloads of smaller transactions (fewer than 500 commands). - For larger work loads (transactions with 500-1000 commands), increasing
ReadBatchSizehas little peformance improvement and may introduce latency in the replication process.
Our recommended values for the two properties are as follows:
- Set the
PollingIntervalto86399seconds (1 day).
- If the activity on the source is very high and disk usage becomes an issue, this may need to be set to a more frequent interval.
ReadBatchSizeshould be estimated based on the average number of transactions made on the database per day.
Step 2. Update the Properties in SQL Server Management Studio
-
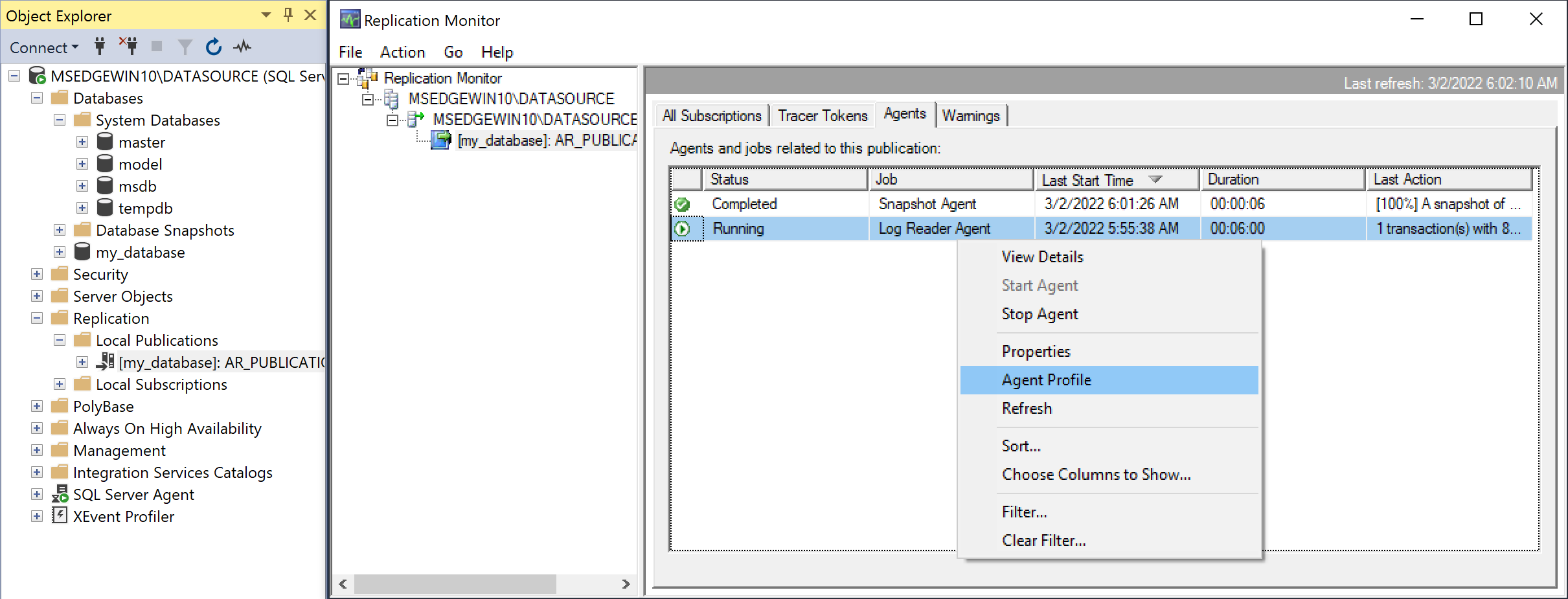
Expand the Local Publications folder, and then right-click and select Launch Replication Monitor.
-
Under Agent, choose Log Reader Agent.
-
Right-click on the pertinent record, select Agent Profile
- Select the pertinent profile and set the
PollingIntervalandReadBatchSizeaccordingly.