Pipeline Refreshes
When a pipeline is refreshed, Etleap either extracts all the data from the source or reprocesses the previously extracted data without ingesting it from the source. During this process, Etleap creates a new version of the pipeline that operates at the same time as the current pipeline version.
Pipeline refreshes trigger for various reasons in Etleap including:
- Incompatible script changes that necessitate transforming the data from scratch.
- To re-establish consistency between the source and destination by capturing deletes for some source types.
How are Refreshes Triggered?
Pipeline refreshes can be triggered from the pipeline’s Overview page. Within that page, you have two options: trigger a manual refresh or set a periodic refresh schedule.
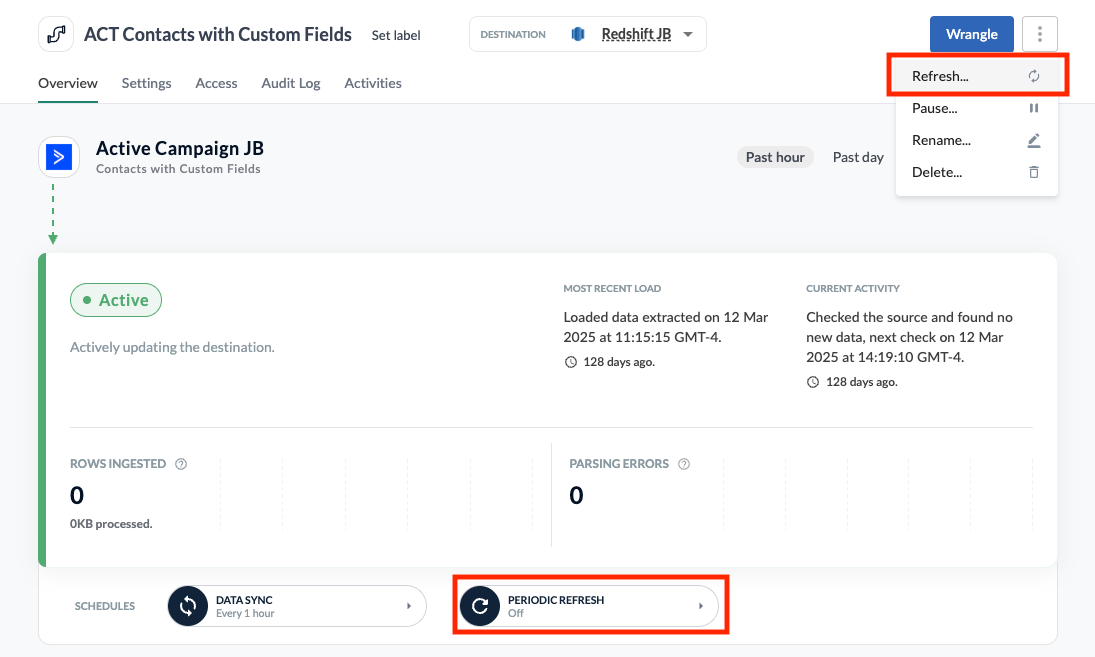
Manual Refreshes
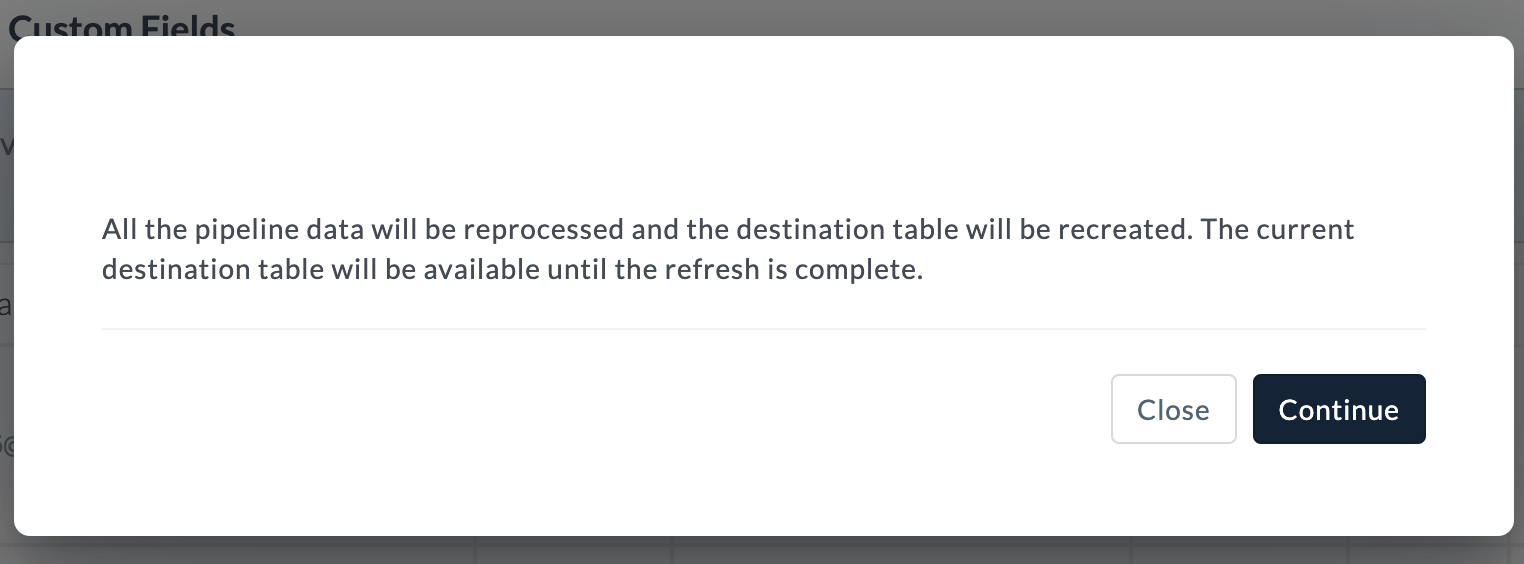
To trigger a pipeline refresh instantly, select the three-dot menu and then click Refresh. Confirm your choice by clicking Refresh Now.
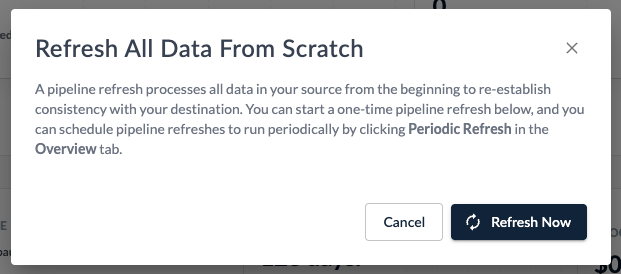
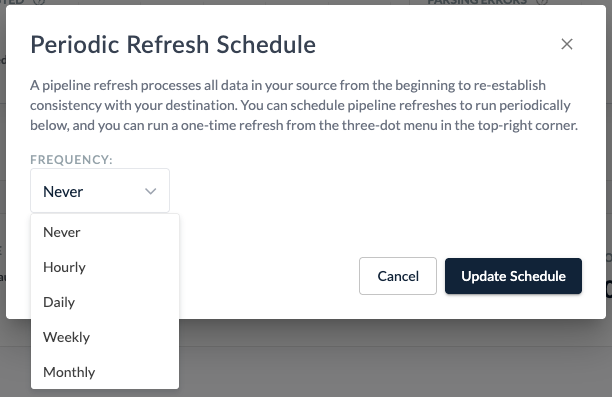
Setting a Refresh Schedule
To configure a pipeline refresh schedule, select between Hourly, Daily, Weekly, or Monthly options and click Update Schedule. Regular refreshes are useful for source types that contain unwanted deleted data.
Incompatible Script Changes
Some script changes require all of the data to be reprocessed. These types of script changes will automatically trigger a pipeline refresh when they are applied. When you update the script in the Wrangler, Etleap will indicate whether a refresh will be triggered before you confirm the script change.
Bulk Refreshes
You can also start refreshes for many pipelines at once on the pipeline list page. When refreshing pipelines in bulk, you have the option to keep the already extracted data.
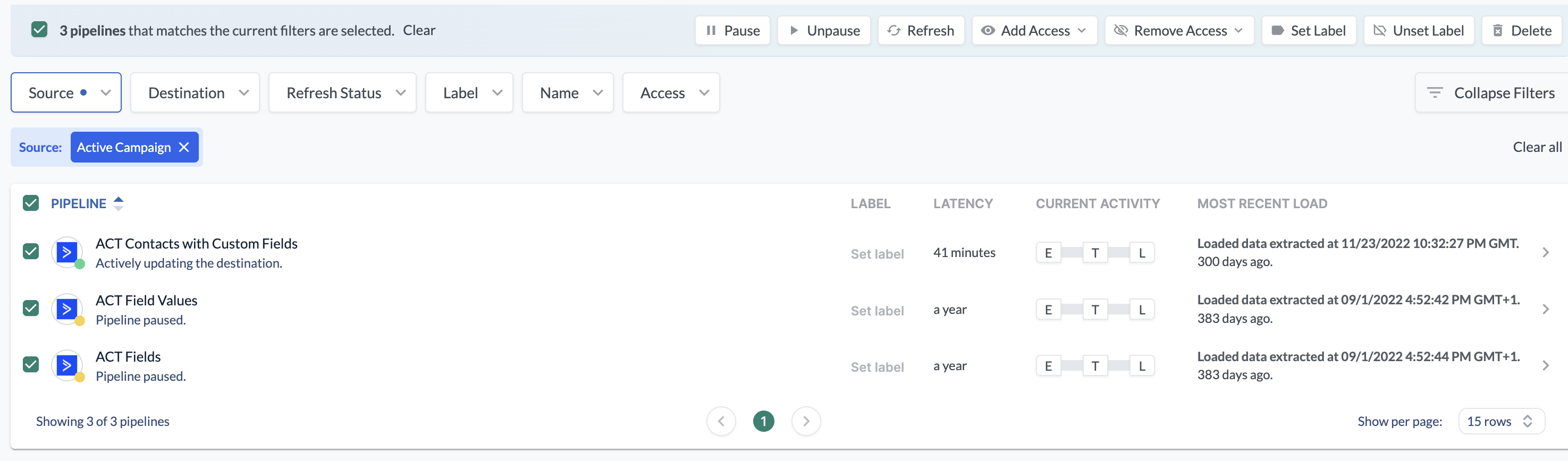
If a refresh is already in progress, Etleap will cancel it and trigger a new one.
Keeping Extracted Data
Etleap can keep the existing extraction data and only reprocess the transformations and loads, depending on the way you trigger your pipeline refresh. See below for details.
| Refresh Type | Keep Extracted Data |
|---|---|
| Refresh Schedules | No |
| Incompatible script change | Yes |
| Manual Refresh | No |
| Bulk Refresh | User decides |
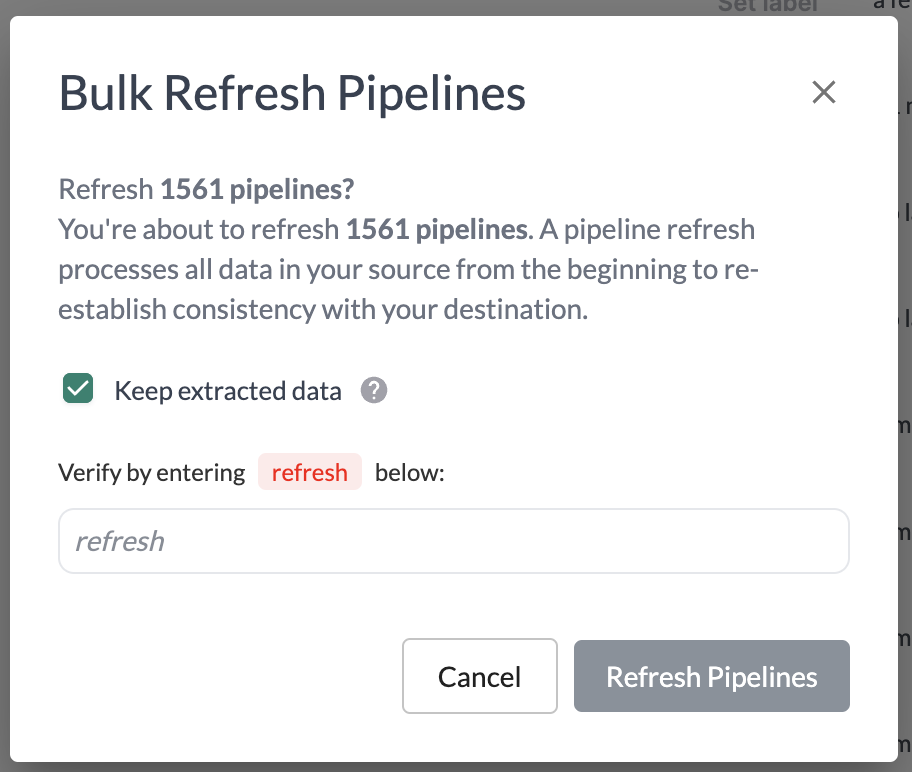
What happens during a Pipeline Refresh?
When your pipeline starts a refresh:
-
Etleap reprocesses all available data in the source, and loads to a separate location in the destination so that your current destination table can continue to be updated.
- For warehouse destinations, the data processed for the refresh is loaded to a temporary table, with a name like
n8FJv3aC. - For S3 lake destinations, the data will be loaded to a separate path under the next version number.
- For warehouse destinations, the data processed for the refresh is loaded to a temporary table, with a name like
-
The current location in your destination will continue to load new data with a few caveats:
- If the refresh was triggered before the pipeline completed its initial load, the initial load terminates, and only data for the refresh processes.
- If the refresh was caused by a script change, the existing location is updated with data processed by the old version of the script, while the refresh location will be updated with data processed by the new script.
- If another schema change is made to the old version of the script while the refreshing pipeline is using the new version of the script (from step 2), the data flow for the current location will stop and only the refresh will be processed. This is because a newer version of the script already exists for the refresh so the script being used for the existing location cannot be updated.
-
Once all of the data in the source has been processed and loaded to the refresh location, the refresh completes. For warehouse destinations, the destination table is atomically replaced by the temporary table.
When there’s a pipeline refresh in progress you can see its status inside the pipeline overview page.
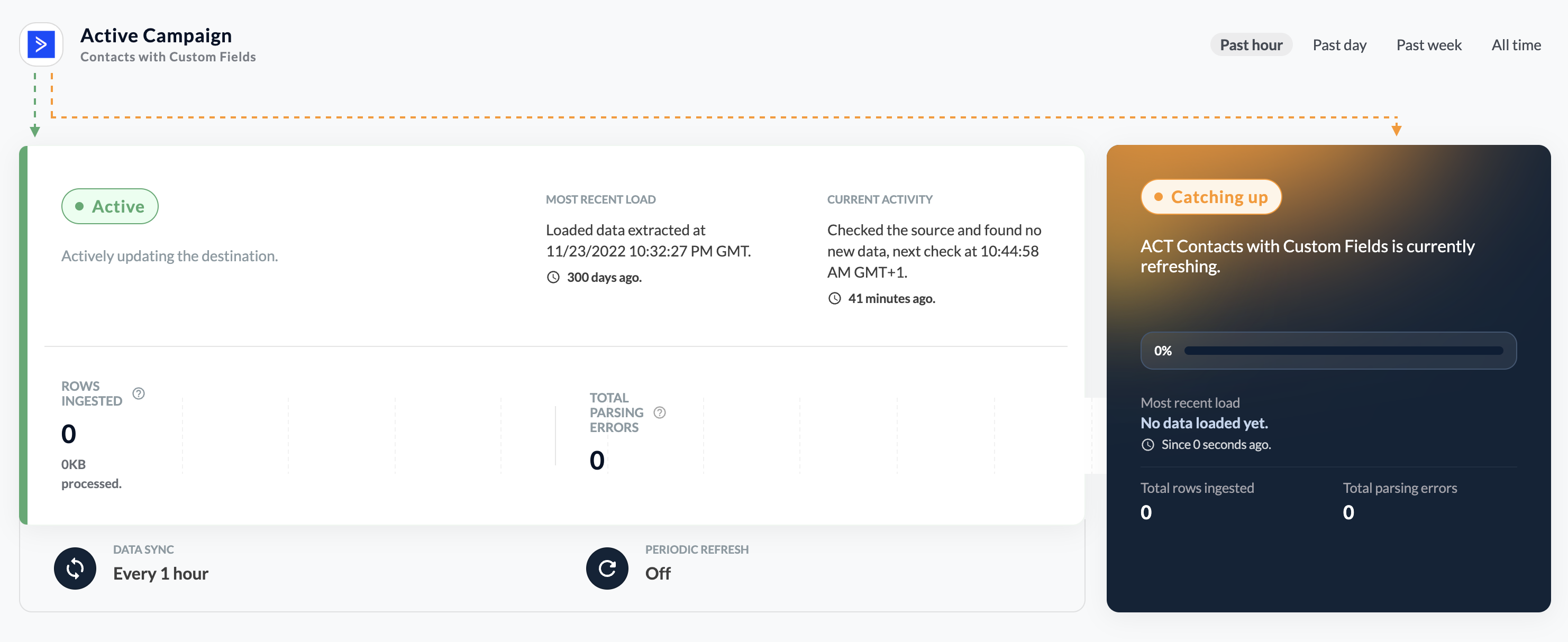
The refresh’s activities can be seen inside the Activities (Refresh) tab.
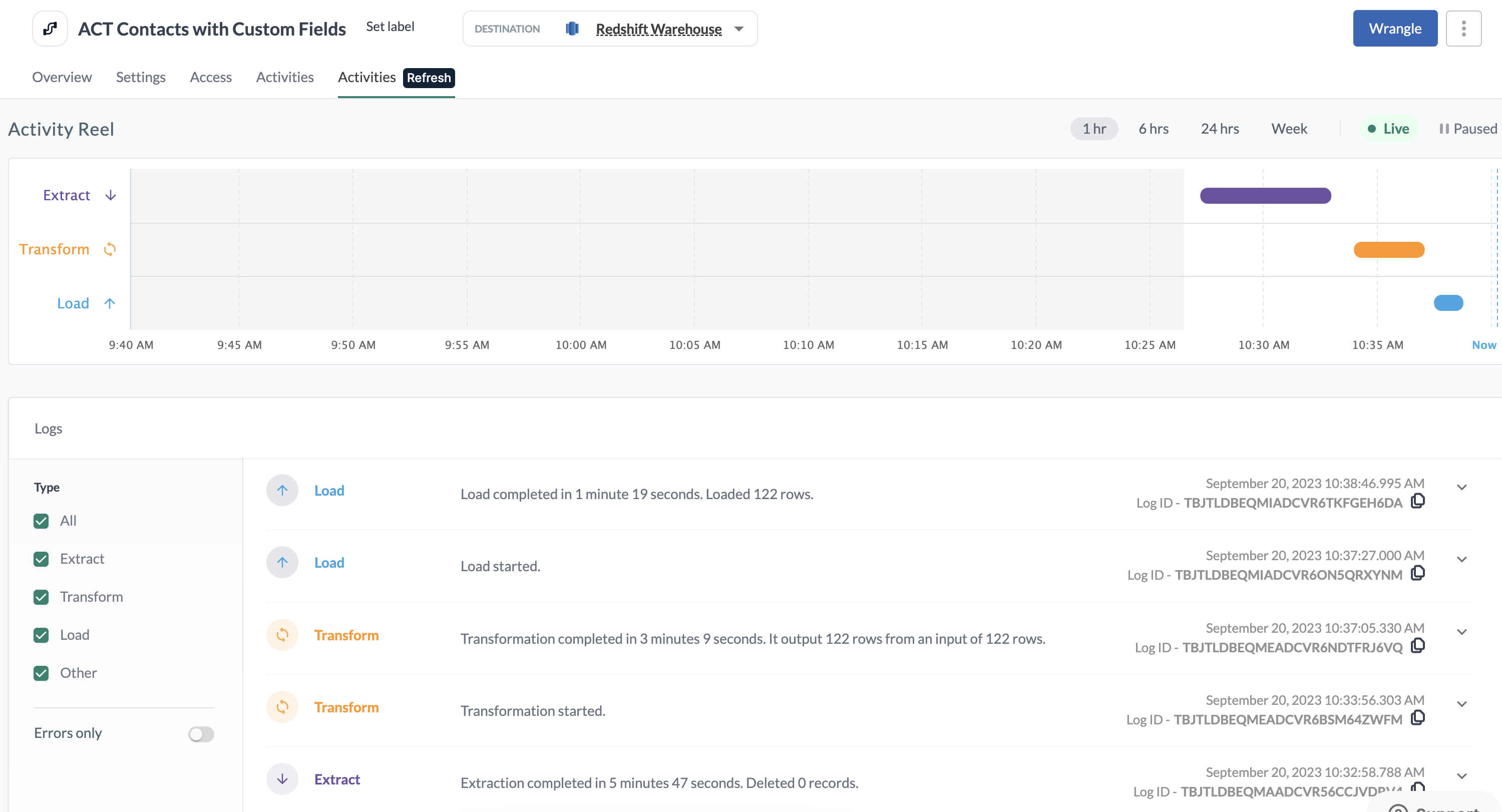
Once the pipeline refresh is complete, the refreshing pipeline version becomes the current pipeline version and only the activity history for the latest refresh is shown in the UI.
There can also be a substantial amount of data that needs to be extracted, transformed, and reloaded during a refresh. In order to optimize the refresh process, Etleap combines all extractions so that the transformations and loading are only done once.
Extractions are not combined during the refresh of some types of pipelines and connections.
- Replace mode pipelines, since each extraction contains all of the data.
- History retaining pipelines, to avoid re-writing the historical record.
- Sharded JDBC connections, to avoid losing the sharding information.
- Mixpanel pipelines, due to Mixpanel’s API configuration.