Connection Setup
Etleap supports ingesting data into Databricks SQL Warehouses (formerly SQL Endpoints) and Databricks All-Purpose Clusters.
Etleap connects to Databricks via JDBC. In order to setup a Delta Lake connection in Etleap you will need the following properties:
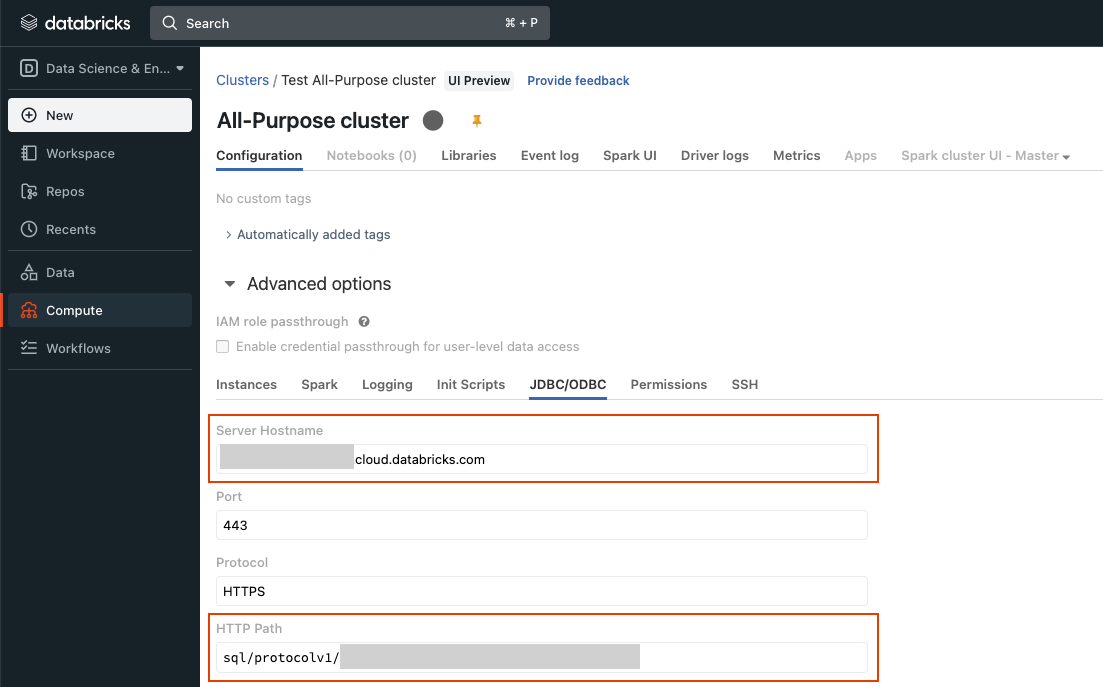
- Hostname: The address of the server to connect to.
- HTTP Path: The Databricks compute resources URL which is specific to your SQL Warehouse or All-Purpose cluster.
- Personal Access Token: Authenticates the user that you want to connect to Databricks with.
Step 1. Get Hostname and HTTP Path
You can find the connection information for your SQL Warehouses and All-Purpose Clusters at the following locations in your Databricks workspace:
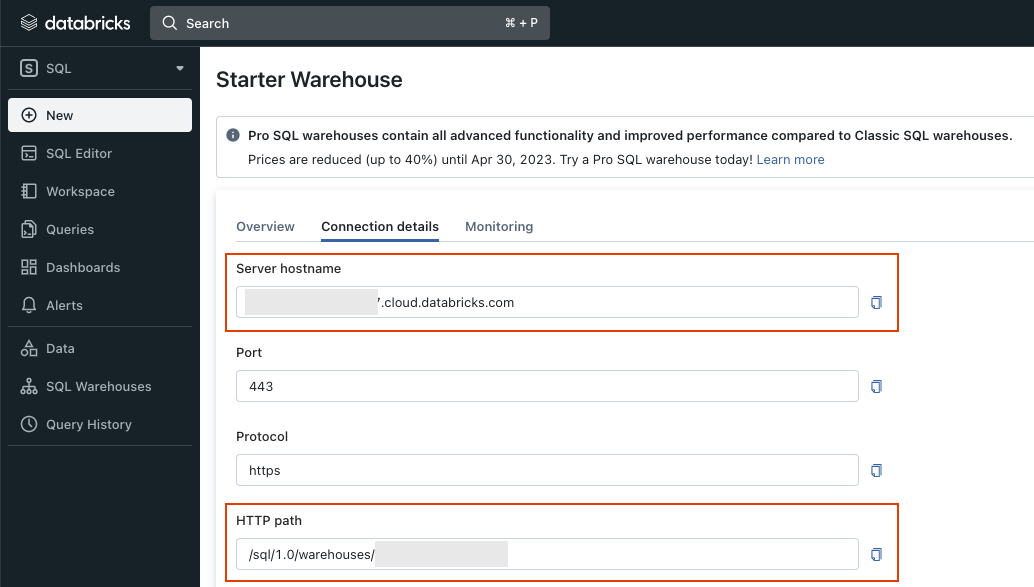
SQL Warehouse
- To retrieve the connection information for SQL Warehouses, go to the SQL Warehouses page in Databricks’ SQL view.
- Select the SQL Warehouse that you want to connect to.
- You can find the hostname and HTTP path in the Connection details tab.
Step 2. Generate a Personal Access Token
Instructions on generating a personal access token, that authenticates your Databricks user, can be found here .
Step 3. Grant write access to a schema
The user configured via the Personal Access Token in the Etleap connection must have write access to at least one schema in the SQL Warehouse or cluster.
The user must either be the owner of the schema or have CREATE and USE privileges on the schema.
Create a new schema with the current user as the owner with:
CREATE SCHEMA <schema_name>;Grant write access to a schema with:
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA <schema_name> TO <user>;
GRANT CREATE ON SCHEMA <schema_name> TO <user>;Key Considerations
Runtime
All-Purpose clusters are only supported with a Databricks Runtime version of 11.0 or higher.
Unity Catalog & Metastores
Etleap supports loading data to Databricks’ Unity Catalog and Hive metastore. During the Databricks connection setup, you can specify the catalog that the connection should use. This allows you to utilize Unity Catalog’s 3-level namespace (catalog, schema, table).
If a catalog is given, it will be assumed that Unity Catalog is available to the cluster. Leave the Catalog Name blank to have the connection use the default Hive metastore.
Managed & External Tables
Etleap will create managed tables in your Databricks Delta Lake destination. This means that the table’s data and metadata will be managed by Databricks.
Etleap does not create external tables in the destination. You can control the location of the destination table’s data by selecting a schema that specifies an external location when creating the pipeline in Etleap. A schema with an external location can be created in Databricks with:
CREATE SCHEMA <schema_name> LOCATION <location_path>;Failing loads
The loads, performed by Etleap, into Databricks Delta Lakes are eventually consistent and not atomic.
If a Delta Lake load fails, there are no guarantees on the state of the destination table and any subtables the pipeline may create. In the case of a failed load, some or even all of the data might have already been loaded successfully to the destination tables. However, Etleap guarantees idempotency for Delta Lake loads: when the failed load is retried, any data that is already loaded will not be loaded again.
In the case of a successful load, Etleap guarantees that all data processed up to the loaded batch’s watermark has been successfully loaded into the destination tables.