Remove Invalid Data
What Is Invalid Data
Invalid Data demonstrates one or more of the following characteristics:
- it was incorrectly generated
- it may be incomplete or look unrelated to the rest of the column
- it has inconsistent format
- it is incompatible with the transformation you want to perform
Signs of Invalid Data
Sometimes the Wrangler cannot identify the data type. This usually happens when the same column has values in different formats. The Wrangler then displays the most permissive format, which is typically a string.
There are multiple ways to deal with invalid data, each of them deriving from one of the following choices:
- replacing invalid data with another value
- removing it completely and excluding the affected records from the dataset
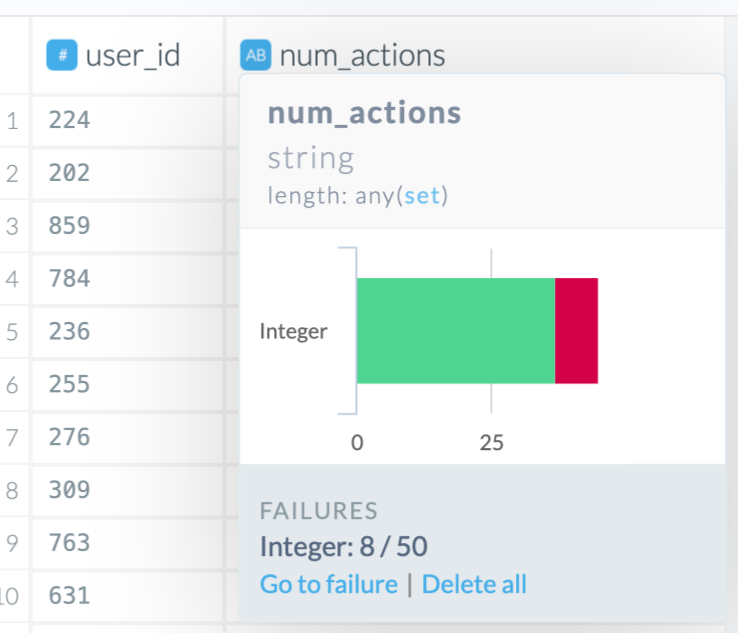
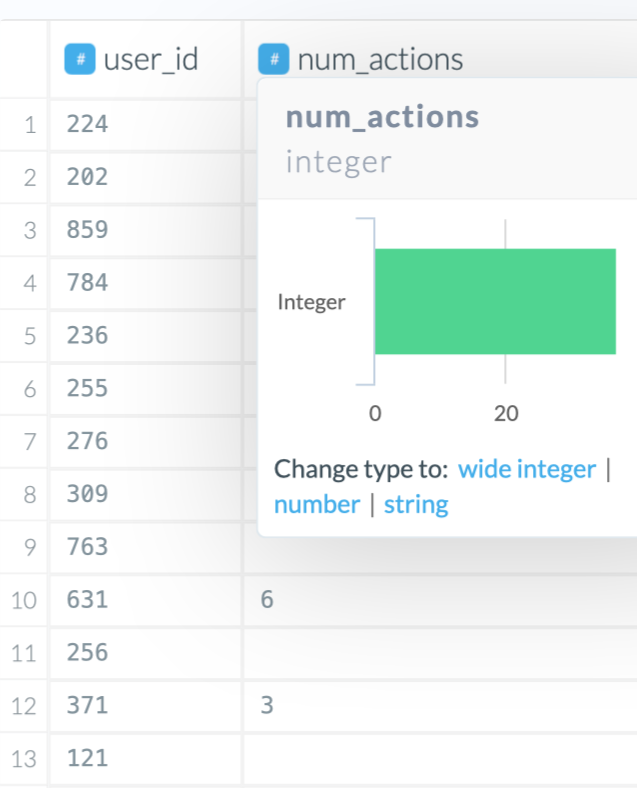
If the column type is not what you expected, click on the type icon in the column header. A small chart will appear. If a column is mostly of one type but not all, it will show how many records in the sample could not be parsed as that type.
The following example illustrates a possible scenario of dealing with invalid data.
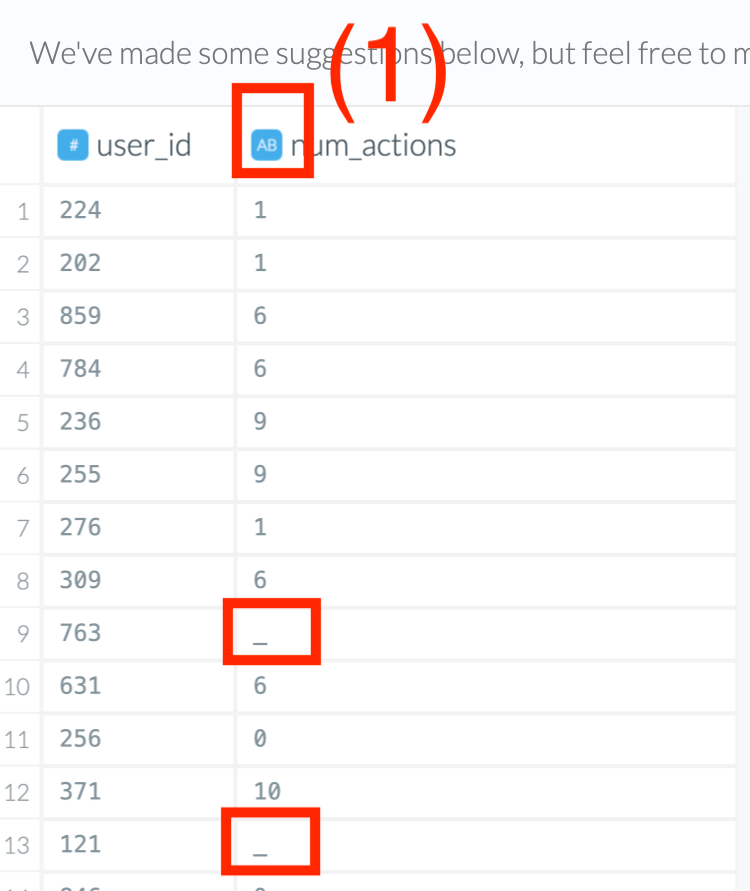
As you can see in the screenshot below, most of the values could be recognized as integers but some could not. Thus, the Wrangler could not assign the type to be integer and chose string instead. Based on our domain knowledge of the column “num_actions”, we know this column should be integer and not string. Let’s explore some options for resolving this.
Replacing Invalid Data
The following methods are all based on the assumption that the data in the affected columns is set as a string type - (1) in the screenshot. In our case, we have a column with mostly integers and a few cells having an underscore instead of a number. The underscores caused the column to be classified as a string format.
Edit Text in Columns
You can replace the values that do not fit with the desired column data type with new values in a matching format or replace them with null values. This brings consistency and helps the Wrangler recognize the data type.
Which option you choose depends on what you are going to do with your data afterward.
Sometimes you need null, and sometimes you need 0. These are not the same! If you need to perform aggregations later, using null may exclude the respective rows from an aggregation (for instance, a mean or median), but using 0 will keep them. This can influence the final result of your calculation.
Steps
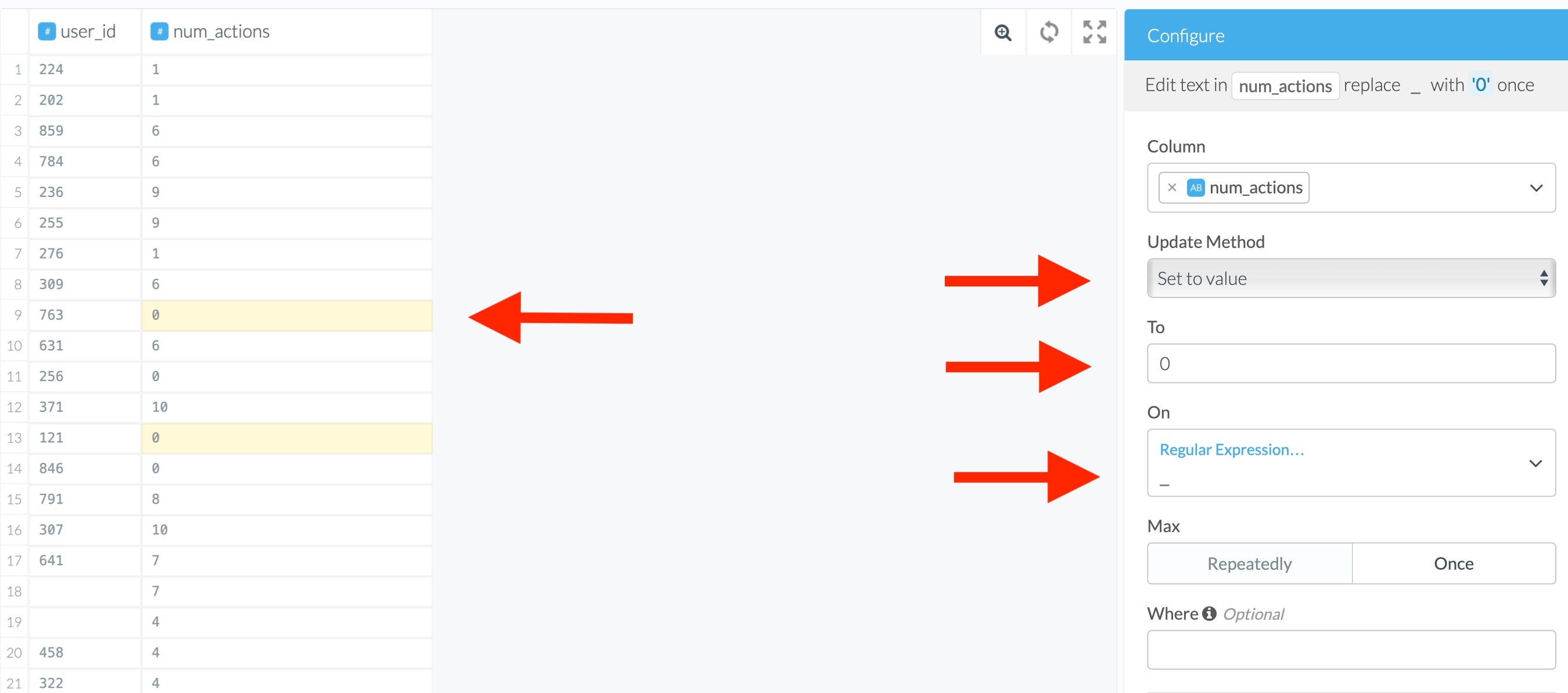
- Find the transform “Edit text in columns” in the Wrangler or type in “edit text” and pick up the top result.
- Select the column.
- In the dropdown menu, select “Set to value” to specify a replacement or “Set to null” to replace with null.
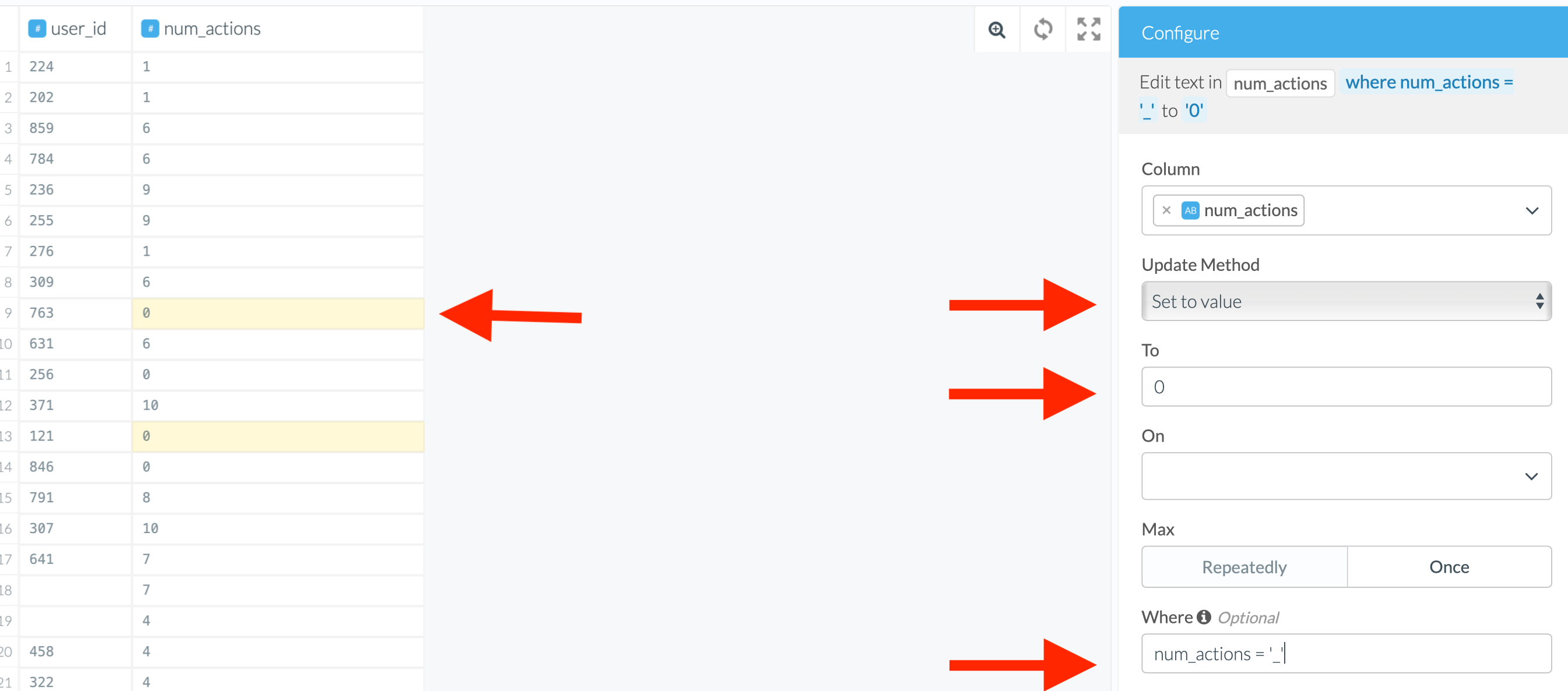
Replacing Invalid Data With a Different Value
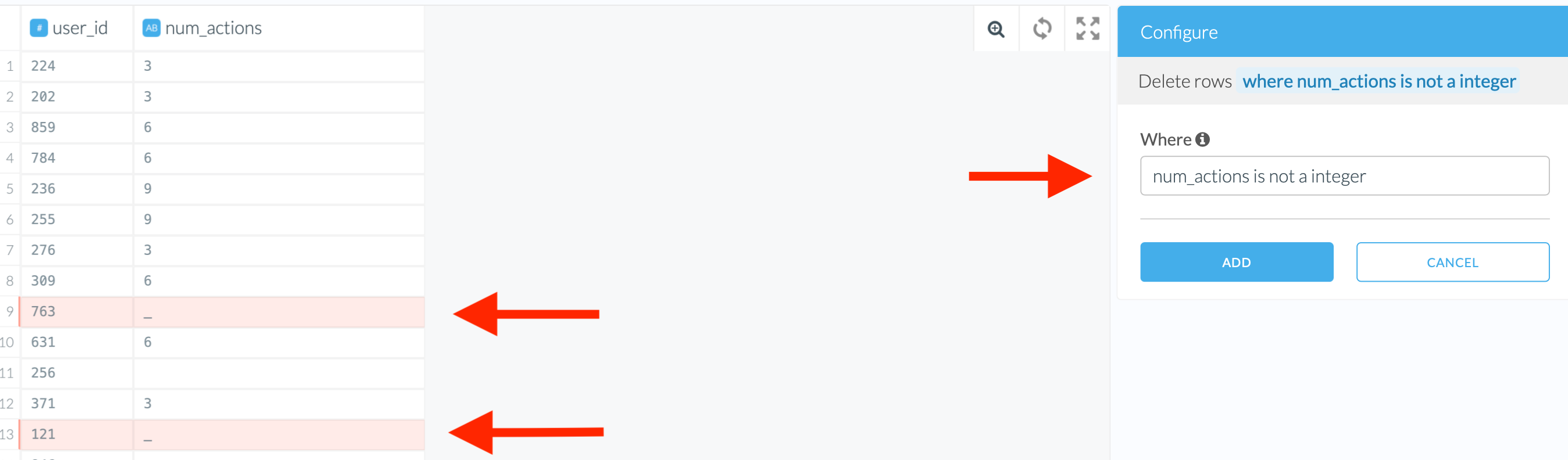
If you choose “Set to value”, you will need to specify the new value as well as a replacement condition. The replacement condition can be set using one of the following options:
- The dropdown menu in the “On” field and, in our case, a regular expression.
- The where clause. Consult the where-clause help (the i icon) to find out about the syntax. Spoiler: it is very similar to SQL!
In the example below, we can even use either of the following conditions:
num_actions = '_'or
num_actions is not an integerBoth of them will lead to the same result of fixing the non-integers.
Replacing Invalid Data With Null
With “Set to null”, you have to use a where clause to avoid losing valid data. The reason is that the replacement is applied to every single row in the column. This would convert a whole column to null values, not only the ones you consider invalid. To avoid this, you need to specify which values you want to replace. You can do it using the where clause with the same conditions as in the previous case.

Cut Columns
With this, you can remove invalid characters from a string, either leaving the affected cells empty or, if there were valid characters in the cell, leaving only the correct ones. Making the values consistent throughout a column allows the Wrangler to detect the proper type for this column.
Steps
- Find the transform “Cut column once” in the script editor or type in “cut” and pick up the top result.
- Select the column.
- Select a suitable option in the “On” field; in our case, a regular expression.
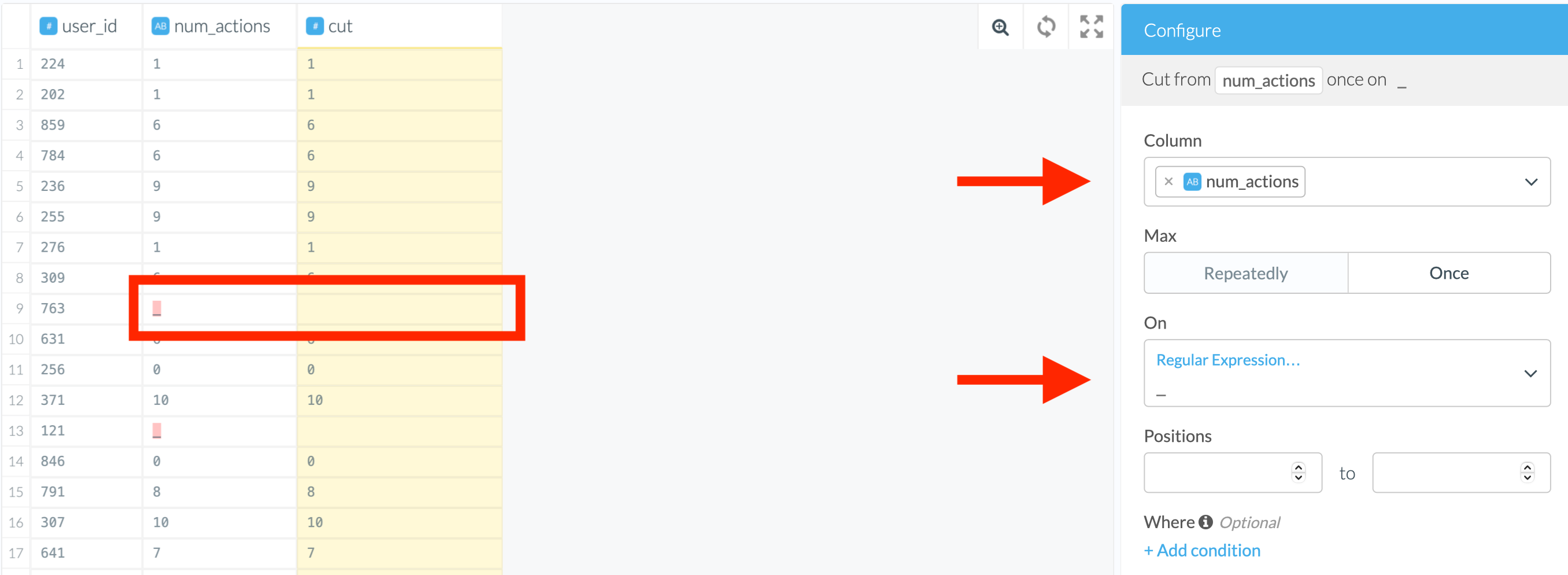
Before we cut the column, it was recognized as a string data type. After the transformation, the Wrangler has set it to integer, and so it will be written into the destination. Etleap defines the destination table type as the one defined in the Wrangler.
Removing Invalid Records
Sometimes you cannot use records with missing data for calculations, regardless of whether you replace invalid values with anything else. In such a situation, it may make sense to get rid of them completely by deleting the rows with invalid data.
Delete Rows
You can use the “Delete Rows Where” transform to remove invalid records.
Steps
- Find the step “Delete Rows Where” in the Wrangler or type in “delete rows” and pick up the top result.
- Select the column.
- Compile a suitable where clause. Remember to use the column name with invalid data in the condition.