PostgreSQL
Etleap supports both query-based extractions and Change Data Capture (CDC) for Postgres. When CDC is explicitly enabled on the source connection, Etleap will use logical replication to extract changes.
Source Setup
Step 1. Create a Database User
Follow these steps to create a new PostgreSQL user with the minimal permissions to read from the schema you would like to access.
- Create a PostgreSQL user. Replace
<user_name>with a username of your choosing. Replace<secret>with a password. You will use these two values later in the connection setup.CREATE USER <user_name> WITH PASSWORD <secret> - Allow the user to connect to the database.
GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE <database_name> TO <user_name>; - Grant usage permission on the schema you will be extracting tables/data from.
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA <schema_name> TO <user_name>; - Grant permission to read from the tables you would like to extract from.
Choose one of the statements below to assign select permissions at a certain level
GRANT SELECT ON TABLE <table_name> to <user_name>; GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA <schema_name> to <user_name>;
You can now use this user to set up a new connection in Etleap.
Step 2. Whitelist Etleap’s IP Addresses
Etleap’s IP addresses must be whitelisted in Postgres. The IP addresses to whitelist are specified when creating the connection in Etleap. Review the IP Whitelisting article for more information on which to use.
Prefer using an API? Go here and select Postgres under the Body header to create your connection via API.
Change Data Capture (CDC) Setup
For PostgreSQL, CDC data is extracted via logical replication. The following section details the steps to configure the database for logical replication.
If you plan to use AWS DMS to capture changes from this Postgres Database outside of Etleap, please follow the steps in this section before creating your AWS DMS Replication task.
Step 1. Configure the Source for Logical Replication
This setup guide should be followed before creating a connection in Etleap with the CDC option enabled. The setup steps for both self-managed and cloud hosted instances are detailed below.
Self-Managed PostgresSQL Instances
- Grant
superuserprivileges to the user used in the Etleap connection setup:
ALTER USER <user_name> WITH SUPERUSER;- Specify the following lines in the
pg_hba.conffile:
# Replace <dbuser> with the username that Etleap will use
# to connect to the PostgreSQL instance
host replication <dbuser> 54.83.203.147 md5
host replication <dbuser> 54.235.178.140 md5- Set the following parameters in the
postgresql.confconfiguration file:
wal_level = logical
max_replication_slots = 10
max_wal_senders = 5
wal_sender_timeout = 0
idle_in_transaction_session_timeout = 0Note that some parameters are static, and you can only set them at server restart. Any changes to their entries in the configuration file are ignored until the server is restarted.
- For PostgreSQL 9, the
pglogicalextension has to be installed. To install it, follow the instructions in the Github repository .
Step 2. Create the _etleap Schema
Etleap must create certain objects in Postgres to support all features of CDC replication.
Etleap will only attempt to create objects in the _etleap schema.
The schema must exist for connection validation to be successful, and can be created in the source with the following statement:
CREATE SCHEMA "_etleap";Schema Change Capture
To detect schema changes for the replicated tables, DDL operations must be captured in the source using the following objects, which Etleap will create in the _etleap schema automatically:
| Object | Name |
|---|---|
| Table | awsdms_ddl_audit |
| Sequence | awsdms_ddl_audit_c_key_seq |
| Function | awsdms_intercept_ddl |
| Event Trigger | awsdms_intercept_ddl |
If necessary, access to the table can be granted to a specific database user with the following SQL statements:
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA _etleap TO {user};
GRANT SELECT, DELETE, INSERT ON TABLE "_etleap"."awsdms_ddl_audit" TO {user};
GRANT USAGE, SELECT ON SEQUENCE "_etleap"."awsdms_ddl_audit_c_key_seq" TO {user};Step 3. Enable CDC for the Connection in Etleap
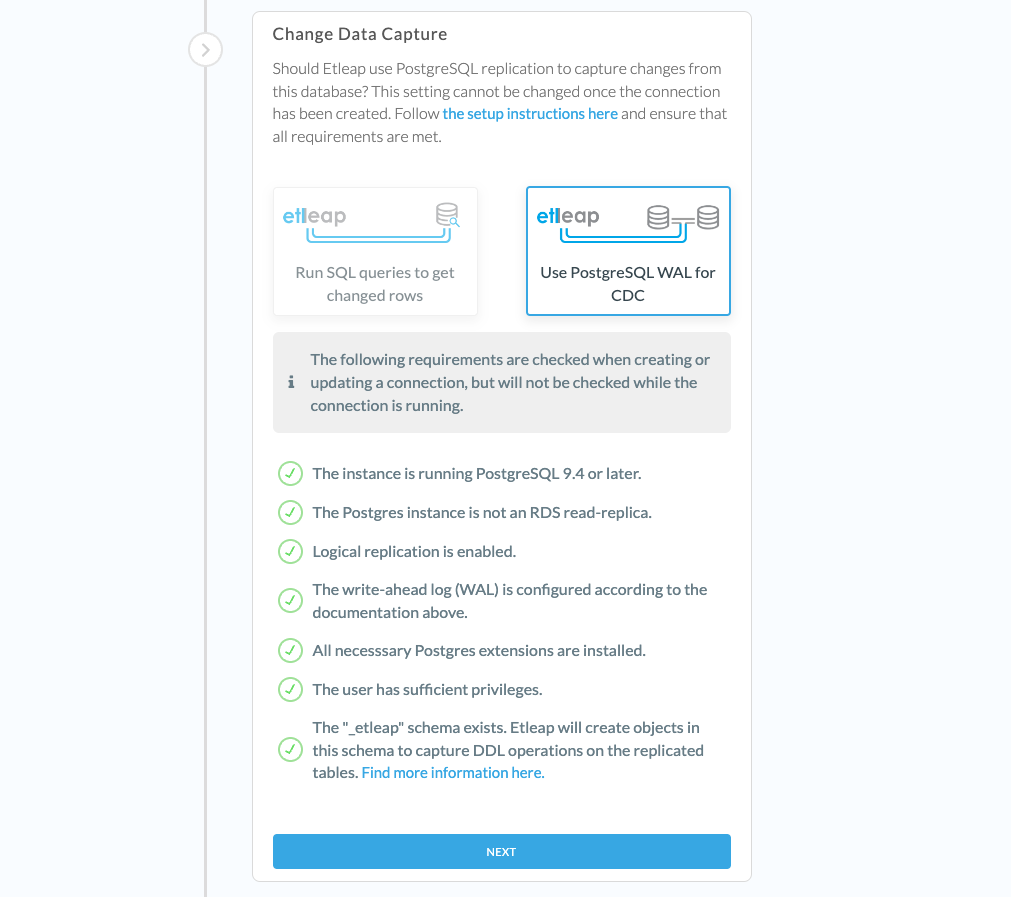
CDC can only be enabled at the time of connection creation. It cannot be modified after a connection is created.
To enable CDC for a PostgreSQL connection, check the following box during the connection setup. The requirements and setup steps listed above will be validated before creating the connection.
CDC Limitations
- Source instance versions earlier than 9.4 are not supported.
- If the instance is hosted on RDS, read-replicas are not supported.
- If you are using Aurora Serverless, v2 is the only supported version for CDC.
- The database password must not contain any of the following invalid characters :
; + %. - If the table contains any LOB columns you will need to change REPLICA IDENTITY of the table to
FULL, otherwise, the LOB column values may be read asNULL. To apply the change use the following query:ALTER TABLE <table_name> REPLICA IDENTITY FULL;
Tables with LOB columns
For Postgres data types that map to a DMS LOB type , such as PostgreSQL’s text, Etleap requires that either the table’s REPLICA IDENTITY is set to FULL, or that database queries are done for the LOBs when records are updated.
Reading LOBs with CDC
To have Etleap read LOB column values directly from the replication logs, set the table’s REPLICA IDENTITY to FULL using the following query:
ALTER TABLE <table_name> REPLICA IDENTITY FULL;Reading LOBs with Queries
If you cannot set the table’s REPLICA IDENTITY to FULL, Etleap can read LOB column values using queries instead.
To do this, enable the option to Fetch LOBs for Updated Rows in the Additional Properties section of your PostgreSQL connection.
When enabled, tables with LOB columns (text, bytea, jsonb, etc.) are eligible as sources for Etleap pipelines even when REPLICA IDENTITY is not set to FULL.
Etleap executes a database query for each updated row during the CDC phase to fetch the LOB values, regardless of the table’s REPLICA IDENTITY setting.
Please note that this reduces CDC throughput and adds additional load on the source database.
The queries that Etleap runs to lookup LOB values when this setting is enabled are of the following form:
SELECT <lob_column_1>, <lob_column_2>, ...
FROM <table_name>
WHERE <primary_key_column> = <value>If the Fetch LOBs for Updated Rows option is enabled on a connection with active pipelines, it is recommended to refresh any pipelines where the source table contains LOBs and does not have REPLICA IDENTITY set to FULL to backfill existing values.
Once this setting is enabled, it cannot be disabled while there are existing pipelines extracting from source tables with LOB columns.
Using AWS DMS outisde of Etleap
If you have an Etleap connection with CDC enabled for this Postgres database and you would like to create a new AWS DMS replication task that captures DDL events (CaptureDdls=true; in your Endpoint settings ), you will need to follow the steps below:
-
Check if there is an
awsdms_intercept_ddltrigger already setup, if not you can skip the remaining steps:SELECT * FROM pg_event_trigger; -
Check the target schema of the
awsdms_intercept_ddltrigger.SELECT n.nspname AS target_schema FROM pg_event_trigger evt JOIN pg_proc p ON evt.evtfoid = p.oid JOIN pg_namespace n ON p.pronamespace = n.oid WHERE evt.evtname = 'awsdms_intercept_ddl' -
If the query above returns
_etleap, you should delete the trigger to ensure your AWS DMS replication task captures DDLs correctly. This will not interfere with Etleap’s DMS task, and Etleap pipelines will still be able to capture DDL events correctly.DROP EVENT TRIGGER awsdms_intercept_ddl; -
If the query above returns something other than
_etleap, you probably have an existing AWS DMS replication task for this Postgres Database. You should create the new AWS DMS replication task with the following endpoint settings:CaptureDdls=true;DdlArtifactsSchema=<target_schema>;
Type Mapping
The table below shows how PostgreSQL data types map to Etleap data types.
Mapped Values
| PostgreSQL Type | PostgreSQL Aliases | Etleap Type |
|---|---|---|
| bigint | int8 | INTEGER |
| boolean | bool | BOOLEAN |
| character [ (n) ] | char [ (n) ] | STRING(n) |
| character varying [ (n) ] | varchar [ (n) ] | STRING(n) |
| date | DATE | |
| double precision | float8 | NUMBER |
| integer | int, int4 | INTEGER |
| numeric [(p, s)] | decimal [(p, s)] | NUMBER(p,s) |
| real | float4 | NUMBER |
| smallint | int2 | INTEGER |
| text | STRING |
Unmapped Values
Each type listed below does not have a specified mapping and will default to STRING in Etleap.
- bigserial
- bit
- bit varying
- box
- bytea
- cidr
- circle
- inet
- interval
- json
- jsonb
- line
- lseg
- macaddr
- macaddr8
- money
- path
- pg_lsn
- pg_snapshot
- point
- polygon
- smallserial
- serial
- time [ (p) ] with time zone
- time [ (p) ] [ without time zone ]
- timestamp [ (p) ] with time zone
- timestamp [ (p) ] [ without time zone ]
- tsquery
- tsvector
- txid_snapshot
- uuid
- xml
Arrays
Arrays of any type are treated as comma-delimited strings in Etleap.