Legacy Features
Legacy features remain available to use within the application but will no longer receive enhancements. In some cases, these features have been replaced by a newer feature which should be used to suppport any future use-cases. Legacy features and their suggested replacements are listed in the table below.
| Legacy Feature | Feature Type | Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Netsuite (Legacy) | Source Connection | Netsuite |
| Models | Data Modeling | N/A |
Documentation for legacy features has been moved to this page and can be found in the following sections.
Models
Models are ways of persisting the results of an arbitrary query. You may want to do this if you have an analytics workflow or dashboard that frequently performs certain aggregations or joins that take a long time to compute. By creating a model, you avoid having to recompute those aggregations or joins for each query.
In database lingo this is called materialized views. While both Snowflake and Redshift supports materialized views natively, creating it through Etleap provides additional benefits:
- You can easily configure the update frequency in the Etleap UI
- When a query uses a table that’s the result of an Etleap pipeline or model, Etleap can manage the the dependency intelligently:
- You can have the model update when one of the dependencies’ data changes.
- Etleap will automatically handle dependent table name changes and prevent you from accidentally deleting dependent objects.
Model Dependencies
Model Dependencies are models or pipelines that “feed into” your model that Etleap gives special treatment. For example, let’s say you are defining a new model with the following query:
SELECT * FROM my_pipeline_table, my_model_table;
If my_pipeline_table is the output table for the pipeline MyPipeline, and my_model_table is the output table for the model MyModel in Etleap, then MyPipeline and MyModel are dependencies of this new model.
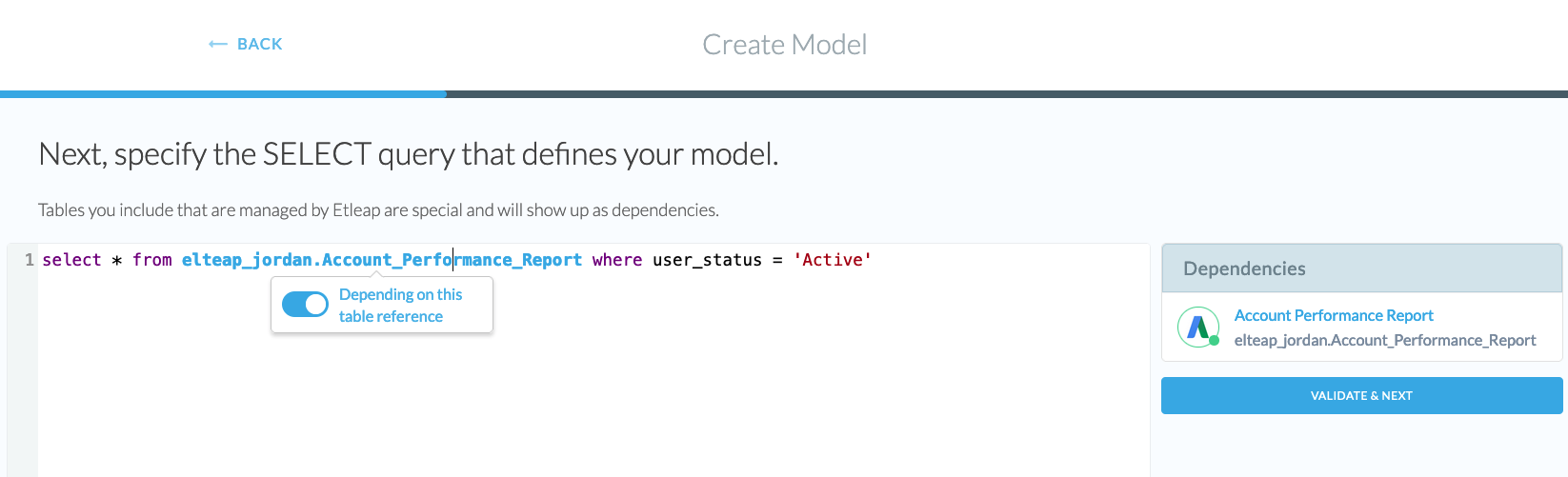
Dependencies offer the following benefits:
- You can define the model’s schedule to trigger an update when the dependency table gets updated by Etleap.
- When you change a dependency’s table name (in Etleap’s UI), the model query is changed accordingly.
- On the model’s page in Etleap, you can see the status of the dependent model or pipeline.
Model Types
Table Model
Table Models create the output table by running your query as part of a create statement, such as CREATE TABLE etleap.active_users_model AS SELECT * FROM etleap.users WHERE status = 'ACTIVE;
Whenever the model updates, it will recreate the table every time. This is always supported, but can cause significant load on your cluster if the model query is expensive.
Materialized View Model
Materialized Views Models use the data warehouse’s underlying Materialized View structure to allow far faster update times thanks to optimizations for tracking changes to the dependent tables and only processing those incremental changes in the model table.
When a model is first created, Etleap will run the materialized view create statement, such as CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW etleap.mv_active_users AS SELECT * FROM etleap.users WHERE status = 'ACTIVE';
Whenever the model updates, it will run the REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW command.
Not every query statement is supported for materialized views. Check the documentation for materialized views in Redshift or Snowflake
Model Updates
Full Update
A full update is when the model runs the query and stores the result in the output table, replacing whatever was there before. You can define how frequently you want the model to update. There are four types of triggers that will cause a model to execute a full update:
- Initial Update: A full update will always be executed immediately when the model is created.
- Update Schedule: You can set an hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly schedule, and there will be a full update to the model according to the schedule.
- Dependency Change: You can choose to have your model update whenever some or all of its dependencies update. There will be a full update unless the model is an incremental Materialized View.
- Manual One-time Refresh: At any time, you can click on the one-time refresh button and it will immediately begin a full update.
A full update is done by dropping the existing table and creating a new one in a single transaction. Additionally, Etleap looks for views in the warehouse that depend on this model. The views that can be recreated are added back automatically in the same transaction. If the views cannot be recreated (perhaps due to insufficient permissions or the query references columns that no longer exist) then Etleap will send you a notification on how to recreate those views.
Incremental Update
For Materialized View models with a supported query, Etleap runs the SQL command for incrementally updating the materialized view. Unlike for Table models, an incremental update does not require recreating any views that depend on this model, unless you use a Manual One-time Refresh, which does recreate the model from scratch.
Model Update Complete Event
If an admin has set an Outbound AWS SNS Topic in Etleap, then you will receive a MODEL_UPDATE_COMPLETE event whenever the model finishes an update.
Pre-Update Hooks
Etleap models support pre-update hooks, which allows you to intercept model updates via SNS. Etleap notifies you when a model is ready to update, and then you send an event when you want the model to execute the update.
Why use Pre-Update Hook?
Here are some example use-cases for controlling when exactly a model updates:
- Quality control of the source data before the changes are propagated to the model.
- Synchronize updates across models so that the data is consistent even when the models are frequently updated.
- Pre- and post- update analysis to compare what data was changed by the update.
Prerequisites
- You use Redshift or Snowflake as a destination.
- An admin in your organization has set an Outbound AWS SNS Topic in Etleap.
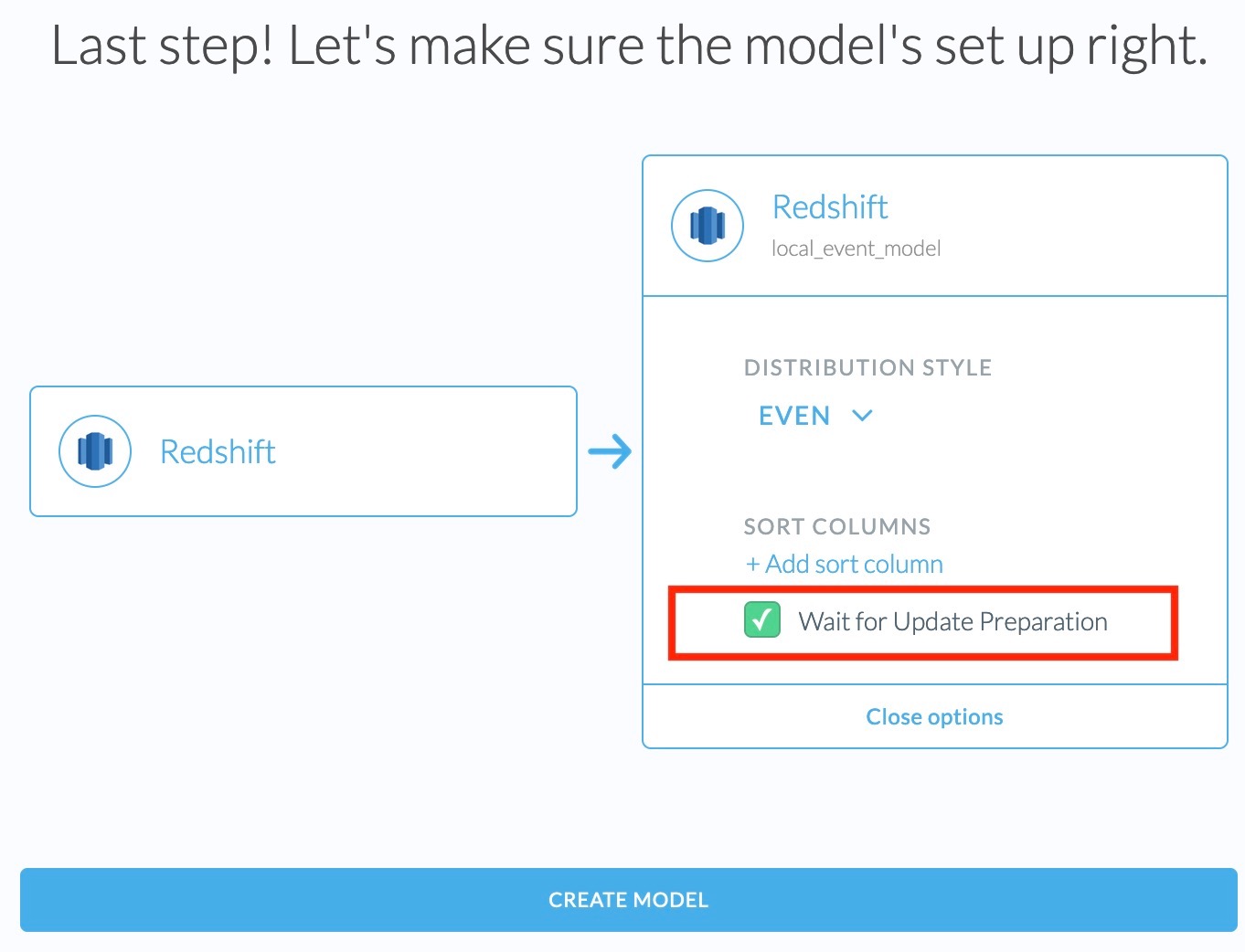
Enable the Pre-Update Hook for a Model
To enable this feature for your model, create your model as usual, but in the last step under destination settings, check Wait For Update Preparation.
Update Flow
Every time the model is ready to update, including the initial update when the model is created, the following steps occur:
1. Model Update Triggered (outbound)
Etleap will send a MODEL_UPDATE_TRIGGERED event to notify that the model’s update conditions have been met.
2. Model Update Preparation Complete (inbound)
After you perform whatever preprocessing you wish, you send an inbound MODEL_UPDATE_PREPARATION_COMPLETE event, and Etleap will execute the model update.
3. Model Update Complete (outbound)
Once the model update is complete, Etleap sends the MODEL_UPDATE_COMPLETE event.
The MODEL_UPDATE_COMPLETE event is always sent for every model, even the models that do not have the Wait for Update Preparation setting enabled.